
1. Data selection
Where possible, the Sustainable Development Report uses official SDG indicators endorsed by the UN Statistical Commission. Where there are data gaps or insufficient data for an official indicator, we include other metrics from official and unofficial providers. Five criteria for indicator selection were used to determine suitable metrics for inclusion in the report :
- Global relevance and applicability to a broad range of country settings.
- Statistical adequacy: The indicators selected represent valid and reliable measures.
- Timeliness: The indicators selected are up-to-date and published on a reasonably prompt basis.
- Coverage: There must be data available for at least 80% of UN Member States with a population greater than one million.1
- Measurability of distance to targets: This must be able to be measured so that optimal performance can be determined.
2. Missing data and imputations
To minimize biases from missing data, the SDG Index only includes countries that have data for at least 80% of the indicators or that have been in previous editions of the SDG Index and have data for at least 75% of the indicators.
Due to the lack of widely accepted statistical models for imputing country-level data for many SDG priorities, we do not generally impute or model missing data apart from a few exceptional circumstances. The list of indicators where imputations have been performed is available online in the Codebook.
Méthode utilisée pour construire l'indice et les tableaux de bord des ODD
The procedure for calculating the SDG Index comprises three steps :
- Establish performance thresholds and censor extreme values from the distribution of each indicator.
- Rescale the data to ensure comparability across indicators (normalization).
- Aggregate the indicators within and across SDGs.
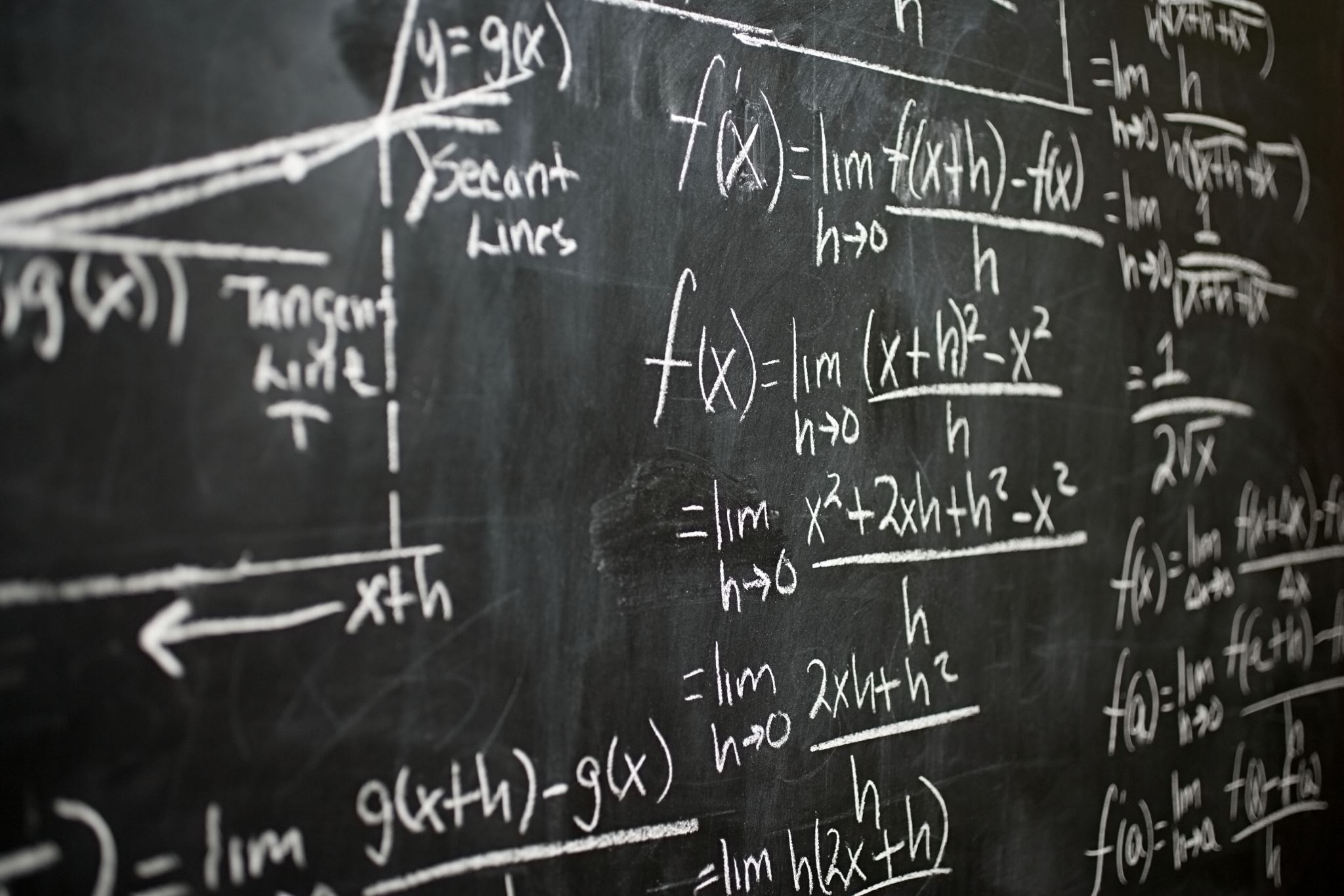
Detailed overview Methodology : https://dashboards.sdgindex.org/chapters/methodology
Méthodologie complète : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sdsna/2018GlobalIndex/m



